During the discussion “Dealing with Disruption: What Every Enterprise Must Consider When Implementing its IoT Strategy, Nader Nanjiani demonstrated how crucial it is for enterprises to understand the IoT deployment user journey. IoT shifts constantly, so a stable understanding of what drives users will illuminate the path to relaying the value of businesses. If an enterprise doesn’t translate data in a user-friendly manner, the value of an IoT investment is lost.
Later during the event HARMAN Connected Services delivered the presentation Mastering integration: building synergy between user experience and IoT. Vaijayanthi Iyengar offered a roadmap to guide enterprises in the identification of current work flows and pain points. She further outlined best practices to spot areas of opportunity for end user and enterprise applications.
Designing digital experiences in the context of enterprise IoT introduces new challenges based on the scale and complexity of the system that go beyond traditional User Centered Design approaches. This process requires moving from ethnographic processes about human empathy to participatory methods for community empowerment; from isolated task analysis in controlled environments to understanding the expertise of a collective in manufacturing/industrial settings allowing automation in specific situations without decreasing the level of autonomy of people. Finally, moving from closed software solutions to self-aware platforms that can react and learn.
Some of the most common pain points that HARMAN International found through user- centered research in this context were: poor understanding about how people interact in the workplace, misunderstanding the use of hardware, lack of a common nomenclature and standardization in the development process to connect the isolated systems in digital platforms, repetitive activities due to the lack of automation, and absence of smart analytics that can use the connected data to track, predict, and react.
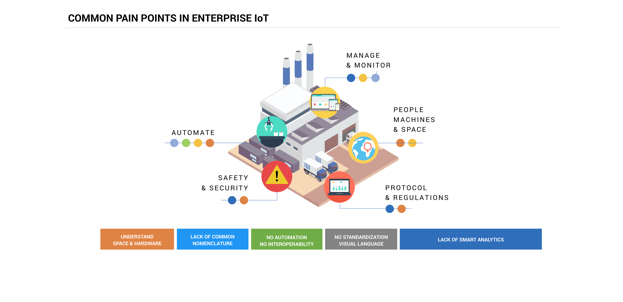
Finally, two case studies were presented: A cross platform software for multicomponent systems that enables collaborative options for software and hardware integration with a new standardized programming visual language and a manufacturing interconnected system with multiple touchpoints that increases the safety and efficiency of the workforce while reducing liabilities and operating costs.
