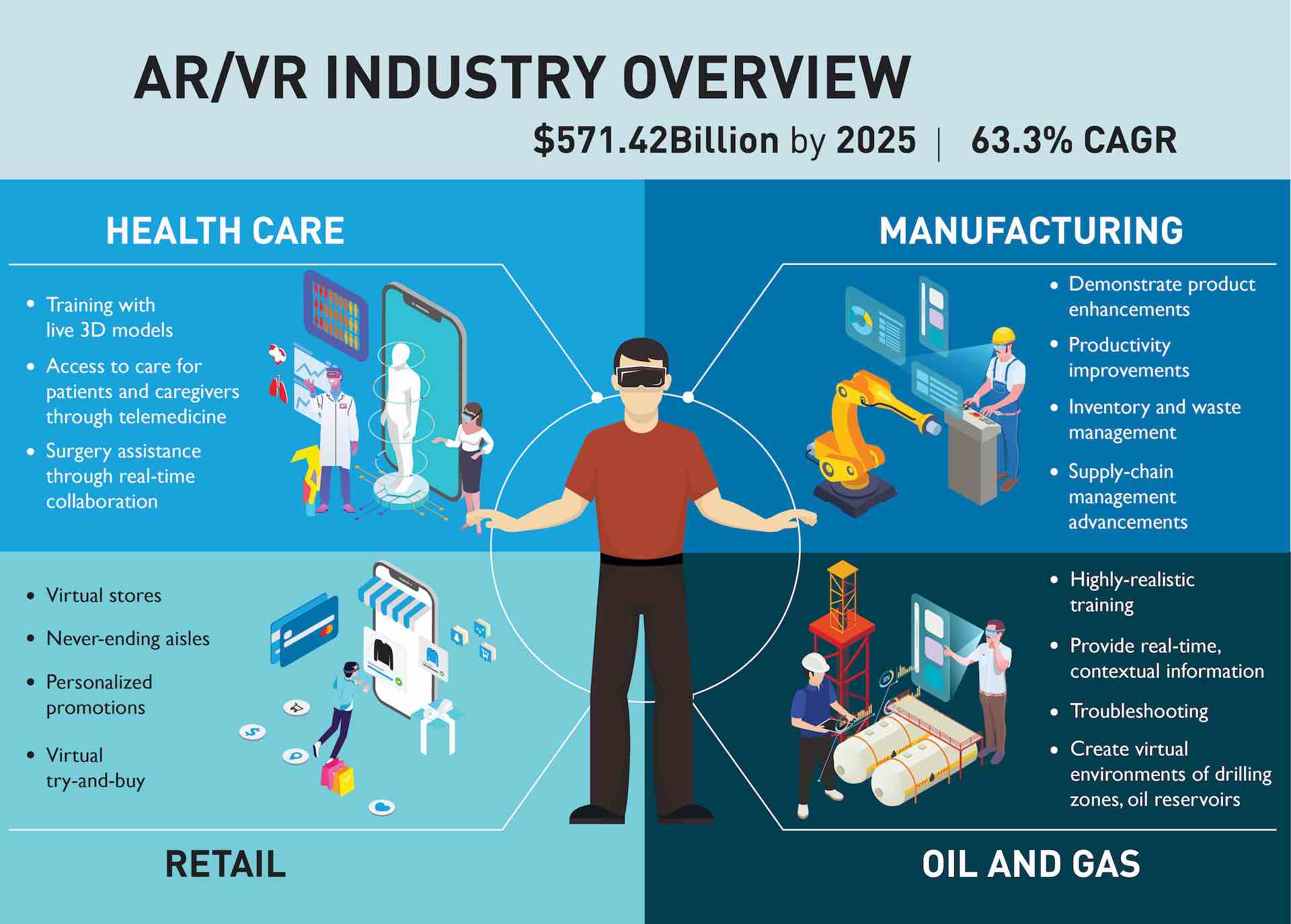
Recent predictions suggest that the Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) market is projected to reach $571.42 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 63.3%. This growth can be attributed to a combination of market drivers such as affordability of AR and VR devices, growing popularity of head-mounted displays (HMDs), rising customer expectations for better content and viewing experience, increasing digitization, and the emergence of supporting technologies like IoT, 5G, and edge computing.
Referred collectively as a single industry, both AR and VR can change the way we see the world around us and generate a lot of excitement across multiple markets. Although AR and VR play a similar role in simulating virtual visualization experience, there are significant differences between the two technologies. AR allows overlaying of digital elements in the real world along with real-time interaction. VR, on the other hand, offers an entirely different simulated experience and can take users to a different world altogether. Simply put, while VR replaces reality, AR complements it.
While AR/VR is mostly associated with gaming and infotainment, they are now widely adopted across several industries to offer immersive customer experiences. Let us look at some of the critical AR/VR use cases in 4 key industries – Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Retail, and Healthcare - that focus on adding value to the business.
Manufacturing: In the manufacturing industry, AR/VR is spearheading a new age of efficiency by simulating almost everything from the factory floor to the final product. AR/VR is often used to demonstrate product enhancements, productivity improvements, inventory and waste management, and even supply-chain management advancements. Both AR and VR help eliminate the need to build full-scale models through rapid prototyping where engineers can assemble and test product components in the virtual world. This reduces time-to-market and results in bottom-line growth as expensive trial and error phases are ruled out. Organizations are now using VR to simulate assembly lines and production processes to identify risky scenarios proactively. With VR, employees can be placed in future workstations, and their movements can be monitored to evaluate task feasibility and proficiency. While VR is used for simulating road and weather conditions by automobile manufacturers to test mechanics and drive quality control, AR is increasingly used to provide guided workflows, hands-on training for faster repairs, and quicker recovery times.
Oil and Gas: The oil and gas industry is continuously challenged by various risks arising out of safety, regulations, market fluctuations, remote work locations, and the hazardous nature of the work. Forced to do more with stringent budgets and being challenged by new clean energy entrants, oil and gas companies are increasingly looking at using AR/VR to streamline operations, improve overall safety levels, and significantly lower operating expenses. AR allows prompt troubleshooting with portable visualized manuals and remote expert assistance. AR headsets help on-field technicians with hands-free maintenance instructions, provide real-time, contextual information and task support for maintaining employee safety. AR and VR are also used for delivering highly-realistic training to identify key drivers of workplace incidents and improve procedural execution by simulating many 'pre-made scenarios. For example, IoT data represented on a 3D model of an oil rig can be used by relevant personnel to proactively identify dangerous substances, manage a leak, or extinguish a fire. Several oil and gas companies are using AR/VR to create virtual environments of drilling zones, oil reservoirs, and other offshore assets. These replicate real-life scenarios like unplanned shutdowns and abnormal operations so that trainees can experience in-person walkthroughs and what-if scenarios to come up with quick emergency responses.
Retail: Virtual stores, never-ending aisles, personalized promotions, virtual try-on – the possibilities of what AR/VR can do in driving customer experiences in retail are endless. When it comes to exploring products and categories for enhancing customer experience, AR is what retailers swear by today. Many large retail companies are using AR/VR to enable virtual try-and-buy that lets customers try on beauty products, clothes, footwear, jewelry, etc., through web cameras. Using 3D imaging and spatial awareness of AR, furniture retailers provide previews of selected furniture at chosen locations within the customers' homes and offices. Many retailers have already introduced in-store navigation features that help customers to find their desired products quickly. Retailers are also exploring options to manage stores situated in remote locations through AR/VR and Robotics to cut down on time and cost of employee travel. Moreover, hands-free vision picking enabled by AR can significantly optimize and simplify warehouse management.
Healthcare: With the rising demand for remote care and at-home medical attention, both AR and VR offer adaptive and agile solutions to the healthcare industry's significant challenges. Some of the best use cases of AR making a difference in healthcare include improved training with remote interactive 3D models, access to care for patients and caregivers through telemedicine, and surgery assistance through real-time collaboration. AR and VR also offer new avenues for physiological and psychological treatment like chronic pain reduction, sleep management, trauma management, etc. On that note, HARMAN, in partnership with Roche, is developing a digital therapeutic platform for people with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), which will focus on behavioral therapy to improve social communication, increase efficiency, and boost personalized access to Healthcare. Seeking to expand the platform for developing other digital health products, HARMAN is also working to provide vision to the visually challenged by offering an enterprise software solution for simulation-based training management.
To conclude
The pandemic has supercharged all things virtual, propelling industries to embrace immersive technologies that offer a hands-free customer experience. However, COVID-19 is also expected to have a mixed impact on the AR/VR industry as some organizations are expected to see a cut in their technology expenditure budget. On the other hand, there is an unprecedented surge in demand for AR/VR-powered remote collaboration tools with the pandemic forcing people to work from home. With faster adoption of the 5G mobile network and the emergence of new software, hardware, and various use cases in the market, the AR/VR concept's dramatic evolution is a high probability soon.
Connect with us to know more.
Authored by:
Yatharth Sahu (Associate Director)
